Product Search
Otsuka Chemical's Chemical Business
With materials at our core, we continue to innovate, developing our technologies and seeking to make products that enable people to live affluent lifestyles. Globally, we provide products to customers in the fields of automobiles electrical and electronic devices, housing and healthcare, focusing on the hydrazine, inorganic materials, composite materials and API intermediates businesses.

Chemical / Material Solution
We contribute to the realization of an affluent society by providing a wide range of products from inorganic salts and other basic chemicals to specialty chemicals such as high-performance polymers, hydrazine derivatives and rubber additives.
Today, the Chemical Solution Department provides many different products such as hydrazine derivatives, rubber additives, polymerization initiators, high-performance polymers and ultraviolet absorbers in addition to the inorganic salts which the Otsuka Group has dealt in since its founding. These products have extensive applications in areas such as healthcare, housing, electronic devices and automobiles.
Our laboratories conduct research and development related to many different materials: the rubber additive ACROAD has been developed at the Rubber Chemicals Laboratory, the high-performance polymer TERPLUS has been developed at the Advanced Polymer Laboratory and hydrazine derivatives have been developed the Technology Development Laboratory. We offer a variety of solutions to customers by customizing the solutions to meet the customers’ needs, ranging from lab scale to plant scale, and strive to make unique chemical products.


We research, develop and manufacture new “materials” and “resin composite materials” in the organic and inorganic material fields.
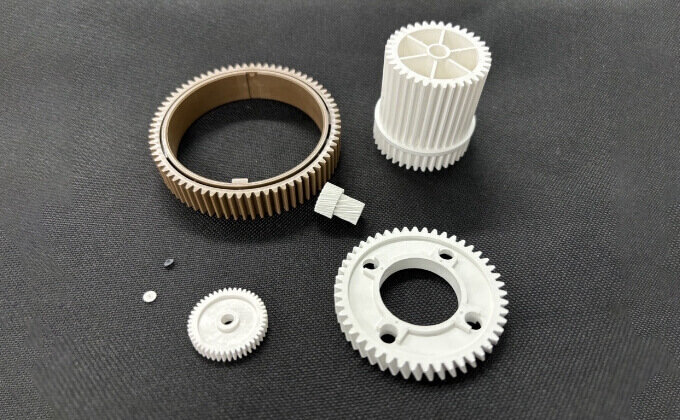
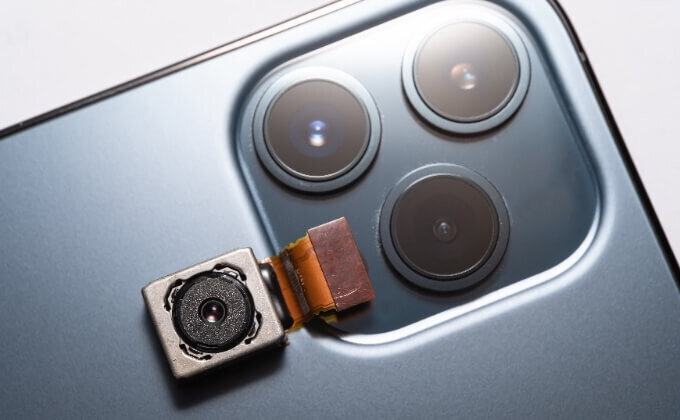
The Material Solution Division is engaged in the research, development, and manufacture of materials and composite materials that are unique in both the organic and inorganic material fields. In the organic materials field, we are engaged in the foaming agent business, while in the inorganic materials field, we focus on the development of ceramics for brake materials, resin reinforcement materials, conductive materials, etc. We are developing, manufacturing, and selling products that evolve from the micro world to the nano world. In addition, utilizing ceramics technology, we are also engaged in research and development of plastics with functions such as sliding properties, precision reinforcement, electrical conductivity, and dielectric properties, and are expanding our business to include not only “materials” but also “components” by manufacturing parts by injection molding and modeling using 3D printers.




Life Science
Otsuka Chemical's life science products are used not only in pharmaceutical-related fields but also in a wide range of other fields, including electronic materials, cosmetic intermediates, and food additives and flavorings, and are highly regarded both in Japan and overseas.
Otsuka Chemical's Tokushima Plant owns a pharmaceutical plant that manufactures beta-lactamase inhibitors and is GMP compliant.
We have been inspected and guided by the Japanese and/or U.S. (FDA) government officials, and we are focusing on building a quality assurance system that can contribute to our customers and the international medical business.



Case study / Column of product manufacturing
With materials at our core, we continue to innovate, developing our technologies and seeking to make products that enable people to live affluent lifestyles. Globally, we provide products to customers in the fields of automobiles electrical and electronic devices, housing and healthcare, focusing on the hydrazine, inorganic materials, composite materials and API intermediates businesses.